What Is a Nameserver? The Essential Guide to Understanding Web Traffic Flow
11-10-2023 - BlogsThe Essential Guide to What Is a Nameserver
Have you ever wondered what happens behind the scenes when you type a website address into your browser? This is where the magic of nameservers illuminates the path. The fundamental question, “What is a nameserver?” opens the door to a deeper understanding of how the internet operates at a fundamental level and ensures that you, the user, reach your online destination with ease and speed.
Nameservers are the invisible yet powerful engines that keep the vast network of online information flowing smoothly. As you navigate through this guide, we will delve into the role of DNS nameservers, the essential cogs in the realm of digital communication that translate human-friendly domain names into IP addresses that computers use to identify each other.
Whether you’re a website owner looking to check nameservers for your domain or simply a curious mind aiming to unravel the intricacies of web traffic flow, you’ve come to the right place. Our journey will also cover the practical aspects of how to perform a nameserver lookup and understand the significance behind this process. So sit tight as we embark on this integral ride through the highways of cyberspace, exploring what nameservers are and why they are crucial to your online experience.

What Is a Nameserver?
A nameserver essentially acts as a signpost on the internet, guiding data packets to their proper destinations. Imagine each website as a physical house; the nameserver provides the address or directions so that visitors can find the house easily. When you enter a website’s domain name into your web browser, that name is actually a human-friendly cover for a numerical Internet Protocol (IP) address, which is the true locator for websites on the internet.
Your query hits a nameserver first, which then translates the domain name into its corresponding IP address. This translation is critical because, while domain names are easy for people to remember, the internet itself relies on IP addresses to route requests and data accurately.
The nameserver is a critical component of the Domain Name System (DNS), often likened to a phonebook for the internet. DNS nameservers maintain a directory of domain names and translate them to IP addresses. This is known as resolving the domain name. Without this system, we would be left trying to memorize the numerical IP addresses for every website we wish to visit, a complex and unfeasible task given the vast size of the web.
A Practical Example of how Nameservers Work
When a user types a URL like “https://thedomainrobot.com” into their browser, there is a need to establish a connection between that browser and the web server that hosts the website corresponding with the URL. So since the web servers of the internet, does not use domain names to identify them – but uses IP addresses – imagine the inconvenience if you had to input the actual IP address of a web server every time you wanted to visit a website. Remembering whether it was 159.89.229.118 or 542.346.341.85 would be a nightmare!
This is where nameservers come into play. Nameservers serve the purpose of associating a URL with the IP address of the server in a more user-friendly manner. Typically, a website has at least two nameservers (although more can be used, for extra redundancy). Nameservers may look alot like other domain names, with subdomains, domain and a TLD like the following:
1) lola.ns.cloudflare.com
2) sean.ns.cloudflare.com
But a nameservers could also look a little closer to IP addresses since – in the end, its not something a human needs to remember
1) ns-320.awsdns-42.com
2) ns-1175.awsdns-26.org
Instead of hosting a website, nameservers assist in guiding internet traffic. To demonstrate the functionality of nameservers in directing internet traffic, let’s examine a practical case. Suppose you want to access the thedomainrobot homepage. At first glance, this appears straightforward: you input “https://thedomainrobot.com” into your browser’s address bar and instantly view the thedomainrobot homepage. Simple, isn’t it?
It seems so! – But nonetheless, in the background alot of stuff happens in a very short amount of time – the overall procedure unfolds in the following manner:
1) You type “thedomainrobot.com” into the address bar and hit enter
2) Your browser sends a request to that domain’s nameservers
3) The nameservers respond back with the IP address of the website’s server
4) Your browser requests the website content from that IP address
5) Your browser receives the content and renders it in your browser
To access a website, you initially need to connect to a Domain Name Server (DNS). However, if there’s a problem with the decentralized naming systems responsible for converting hostnames into IP addresses, you may encounter an error message like “DNS server not responding”.
The Use of Nameservers in the Real World
In the real world, the importance of nameservers can’t be overstated – we interact with nameservers daily, often without realizing it. Each time we conduct a simple act, like sending an email, streaming a video, or engaging in online shopping, nameservers facilitate these actions by resolving domain names into IP addresses – a process that is crucial for data to travel across the internet.
When we breakdown “what is a nameserver?” in practical terms, it’s like the internet’s phone directory. Just like you might search for a contact in your smartphone, computers use a DNS nameserver to look up the location of the server hosting the site or services you want to reach – it doesn’t matter if you’re using a computer in New York trying to access a website hosted in Tokyo; the nameserver swiftly connects these two points.
Businesses and webmasters conduct nameserver lookups to ensure that their websites are accessible and resolving correctly for users worldwide. Because without nameservers, the seamless web experience that we’ve come to expect would be replaced with a series of complex, manual lookups that would slow down our access to information and disrupt our online interactions.
Why Use Custom Nameservers?
When businesses grow, they often need a more personalized approach to how they manage their presence on the internet, which includes using custom nameservers. If you’re wondering “what is a nameserver?” in simple terms, it’s a helper that directs people to your website when they type in your web address. Custom nameservers let you use your company’s name instead of the standard address your hosting company gives you. This makes your business look like it has its own dedicated space on the internet, which can seem more professional to customers and partners.
Using the terms “what is nameserver” or “what are nameservers,” we’re referring to the same helpers, but customizing them means you have more control over your website. For example, if you decide to change where your website is hosted, custom nameservers can make this switch invisible to your website visitors. Additionally, a custom DNS nameserver can be configured for better performance and security.
This means your website may load faster for visitors and be less vulnerable to certain online threats. By setting up custom nameservers, you can enjoy a more consistent and secure online experience for your business and your website visitors. This approach is particularly valuable if you prioritize your brand’s strength and reliability on the web. Below we tried to mention a couple of the major reasons, you might wanna use custom nameservers
Security
Have your website ever been the victim of an DDOS attack? Some custom nameserver providers offer protection against these kind of attacks and hacking forays. Therefore, it may be worth considering finding a name server provider that offers extra security so that you can be calm and know that any malicious attack will be prevented by your name server.
A significant proportion of hacker/spam attacks can be thwarted by the name server, resulting in these requests never reaching your web server – meaning your site is better protected against threats such as DDOS attacks, SQL injections, comment spam, etc. And in the end, this results in a fortified and secure environment for your website.
Optimization
Some providers like Cloudflare also offer optimization features to speed up your website. Cloudflare offers Javascript/CSS Minification and Image Resizing – both optimizations that can have huge impact on your websites performance!
Free SSL
In the year 2023, you cant have a website, without having it secured with SSL – having a website without SSL is basicly a SEO death sentence. Most webhosts today, already offers free SSL from Let’s Encrypt or similar. But today its also very common for custom nameserver providers, to offer free SSL, as a part of their service.
Caching / CDN
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a system that stores content such as images, web pages, CSS files, javascript files, videos, etc. on proxy servers. These servers are strategically located closer to the end users, which gives faster access to these things than if the user’s browser had to retrieve all the things on the web server the website is on. Making use of caching / CDNs can often be the difference between a decent and an incredibly fast website.
Embracing Custom Nameservers for Your Website
In today’s digital landscape, having custom nameservers is akin to claiming your slice of online real estate with a personalized touch. There’s virtually no downside to utilizing custom nameservers for any website – they offer an enhanced level of control, bolster security, and improve reliability. Moreover, custom nameservers can contribute to a cohesive brand identity, reinforcing your professional image every time someone visits your site. With the relatively simple setup process and the significant benefits they provide, custom nameservers are an accessible upgrade for any website owner looking to optimize their online presence.
How to Check your current Nameservers?
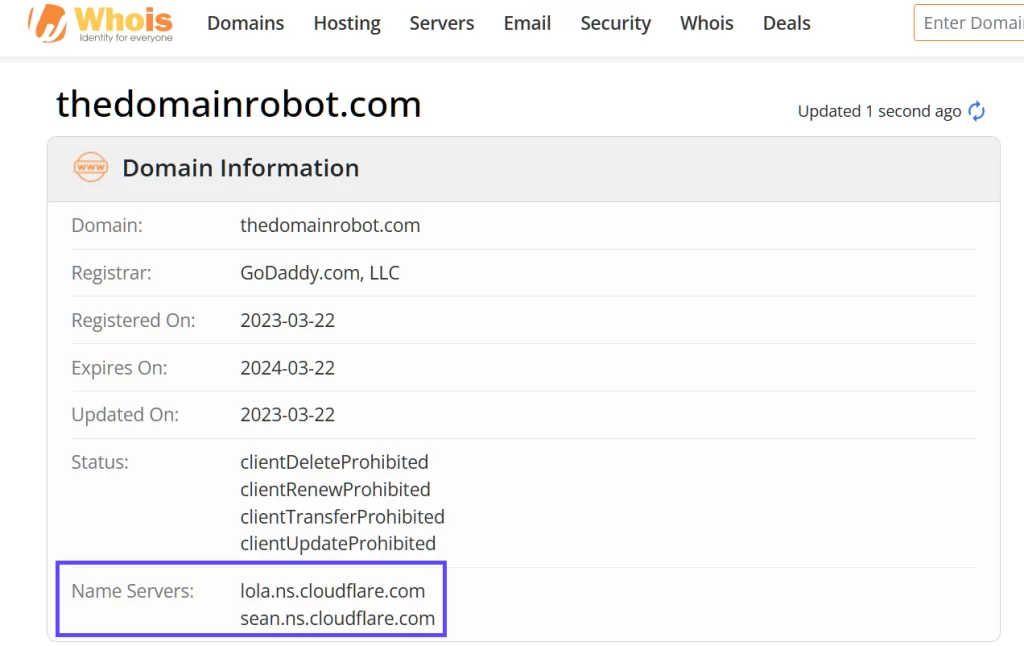
If you’re uncertain about the nameservers you’re presently utilizing, you can verify them via numerous Whois lookup resources by simply providing your domain name.
Whois Lookup
There are countless online whois lookup sites that make it possible to find information about a particular domain. These pages provide varying amounts of information – everything from the domain’s creation, expiration date, the domain’s registrar, the contact information, and many more things. But the vast majority of them list at least the domain’s nameservers.
1) whois.com
2) icann.com
3) who.is
4) whois.domaintools.com
5) thedomainrobot.com
6) mxtoolbox.com
NSLookup, with Windows PowerShell
Another way for the tech savy is the make use of Window’s build-in PowerShell/terminal.
Windows PowerShell is a command-line shell and scripting language developed by Microsoft. It is built on the .NET Framework and is designed for system administration, automation and configuration management. It provides full control over the Windows operating system and many aspects of the server functions. Users can perform a variety of complex administrative tasks remotely, manage files, registry keys, services and processes efficiently. Furthermore, PowerShell supports various commands, also known as cmdlets, which enable you to manage computers from the command line. PowerShell’s scripting language is more complex than the traditional Command Prompt, but it offers a much more powerful and flexible framework.
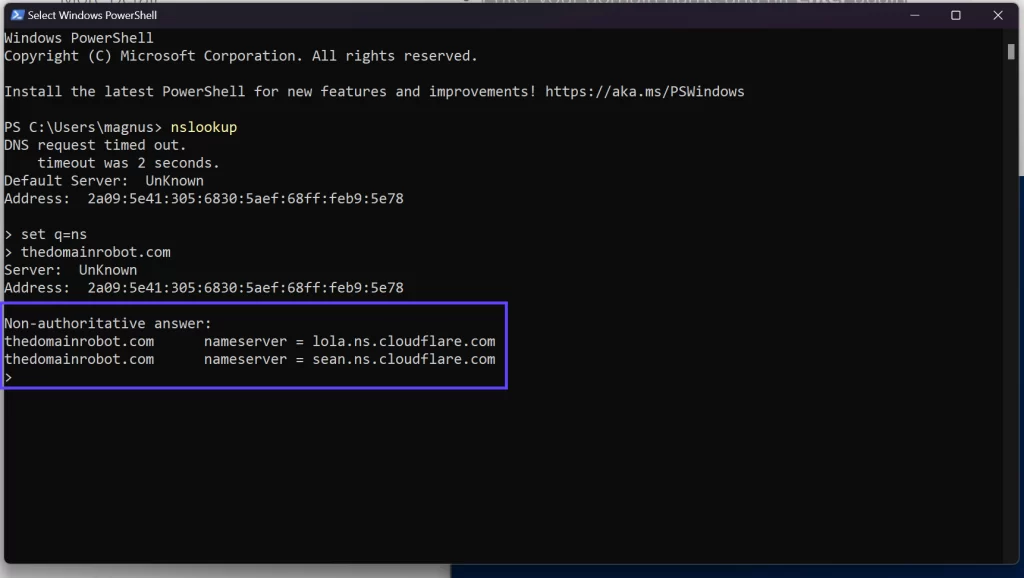
1) Open PowerShell (you can search for PowerShell in the Start bar to launch the program).
2) Type nslookup in the Powershell interface.
3) Type set q=NS and hit Enter.
4) Enter your domain name and hit Enter again.
Host -t NS your-domain-name.com
iOS Terminal is an application that provides users with a command line interface to operate their iOS device. This terminal emulator application allows users to explore their device’s file system, execute system commands, and perform various tasks that are generally not available through the device’s graphical interface. iOS terminal has root access, thus it aids in tweaking or customizing the device beyond the usual settings and parameters. Note that the use of the terminal often requires advanced knowledge or specific instructions to prevent unwanted consequences.
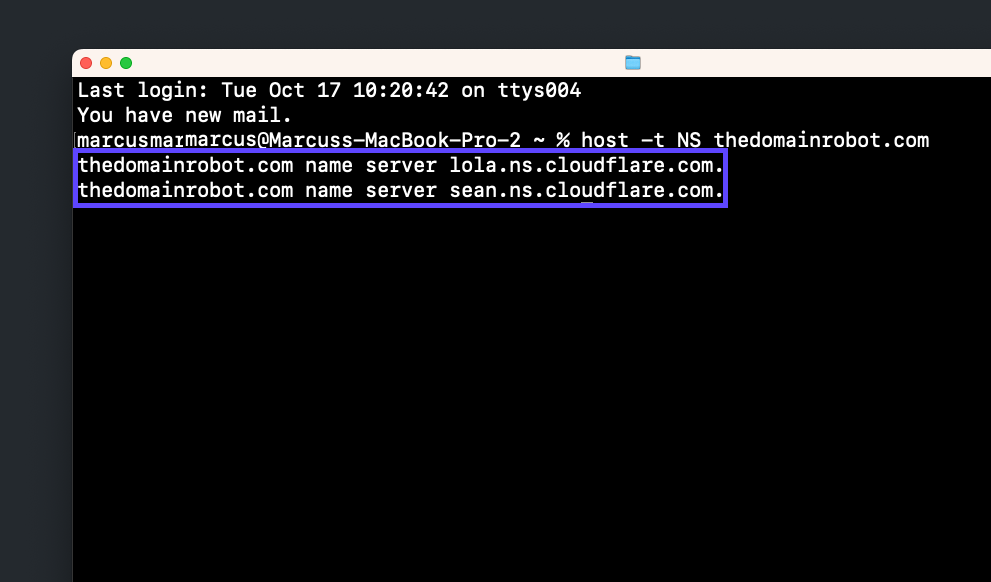
1) Click the Launchpad icon in the Dock.
2) Type Terminal in the search field, then click Terminal.
3) Type in host -t NS your-domain-name.com
4) Hit enter
How Many Nameservers can you have?
Typically, a domain is required to have at least two nameservers for redundancy; this way, if one fails, the other can take over without disrupting access to your website. However, you can have more than two, with many businesses using between two to four nameservers. This setup helps distribute the traffic load and enhances the overall stability of the domain. Ultimately, the number of nameservers you decide to employ should reflect your website’s size, traffic, and your desire for resilience against potential downtime.
Advantages of Multiple Nameservers
Having multiple nameservers is like having a team of experts working to ensure your website is always reachable. When you spread your domain’s information across several nameservers, you’re creating a robust support network. This redundancy means if one server encounters issues, others are ready to step in, keeping your site online without interruption. It’s an essential safety net that provides peace of mind.
Additionally, multiple nameservers can handle web traffic more efficiently. By distributing the workload, each server can operate optimally, potentially speeding up the process of connecting users to your site. This is particularly crucial for websites experiencing high volumes of traffic – extra nameservers can help manage the flow, preventing bottlenecks and slow load times that could frustrate visitors. By enhancing both reliability and speed, multiple nameservers not only improve user experience but also contribute to a positive reputation for your site. Visitors and customers value consistency and efficiency, keys to success in the digital space.