What is a DNS Record?
23-09-2023 - BlogsUnderstanding What is a DNS Record
In the vast network that forms the internet, a term that frequently comes up is “DNS record.” So, what is a DNS record? Think of it as a vital ingredient in the complex recipe that ensures you can visit websites without memorizing a string of numbers. A DNS record acts as a translator between the domain names we type into our browsers and the numerical IP addresses that computers use to identify each other on the internet.
DNS, which stands for Domain Name System, is akin to an extensive directory that keeps track of domain names and their corresponding IP addresses. This directory allows for the conversion of easy-to-remember domain names into IP addresses that computers and other networking devices require for locating resources on the internet. Since this is a very simplified how a DNS works – we wrote a in depth explanation of this concept – a detailed blog about can be found at “What is DNS and How DNS works”
Within this system, a common type of entry is known as a ‘record’ in DNS – each record has a specific purpose in guiding the search of a particular domain name to its numerical counterpart. Therefore, when we ask, “What is a record in DNS?” we’re referring to those entries that keep the internet accessible and organized, enabling us to connect to websites swiftly and efficiently without needing to recall the complex numeric codes that form their actual address on the web. Among the myriad of DNS record types, the most commonplace are NS (name server), A (address), MX (mail exchange), and TXT (text record).
Exploring the Different DNS Record Types
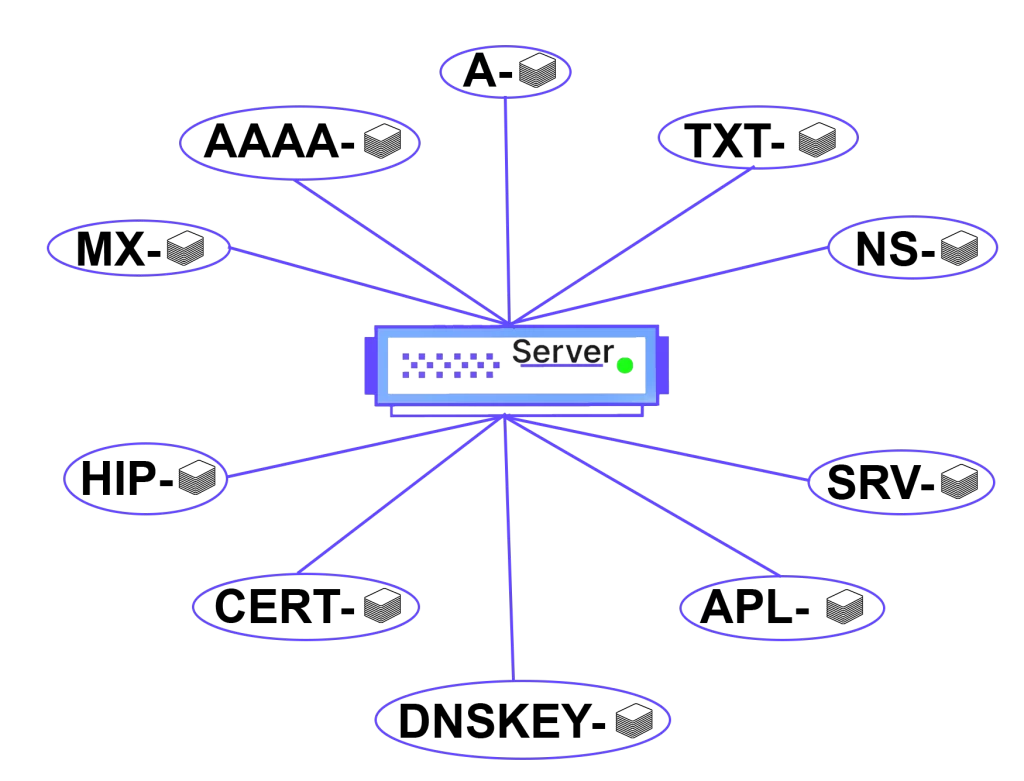
When examining the infrastructure that keeps the internet running smoothly, one inevitably encounters various DNS record types – these types of DNS records form an extensive list, each with a unique role in controlling how traffic is directed and managed across the web. The Domain Name System, or DNS, is like the address book of the internet, containing vital information about where digital resources are located. Just as a contacts app on your phone might have different fields for email, phone number, and home address, the DNS has different record types to specify various pieces of information about a domain.
Each DNS record type serves a specific function, from pointing to the primary server for a domain, to specifying mail server addresses, to providing additional security features. The most familiar types include the aforementioned ‘A Record,’ which links a domain to an IPv4 address, and the ‘AAAA Record,’ its counterpart for IPv6 addresses. But there are many more, each ensuring the efficiency and security of our online interactions – there are currently around 90 different official DNS record, some of them more known and used than others.
Understanding these various types of DNS records is essential for anyone involved in web administration, cybersecurity, and IT infrastructure. They are the mechanisms by which the DNS can swiftly and accurately connect users’ requests with the right destination, enabling what we often take for granted—seamless navigation of the internet.
The most common types of DNS records
it’s beneficial to familiarize oneself with the most common types of DNS records. These records are the essential building blocks that direct and facilitate web traffic within the Domain Name System, making sure that our online experience is smooth and uninterrupted. While the DNS contains a variety of records, certain types are utilized more frequently due to their fundamental roles in internet operations. From linking domain names to IP addresses, to routing email traffic, these fundamental DNS records are the unsung heroes that work quietly behind the scenes.
What is a DNS A Record?
The A record, also known as the address record, maps a domain name to the IP address (IPv4) of the computer hosting the domain. The A record is one of the most commonly used DNS records and is essential for the website’s visibility on the internet. It enables users to access a website using the domain name instead of the IP address.
For instance, when you type a website’s URL into your browser, an A record lookup is performed that retrieves the IP address associated with that domain name, making the website load into your browser.
What is a DNS AAAA Record?
The AAAA record, is similar to an A record, but instead of pointing a domain name to an IPv4 address (as an A record does), an AAAA record points a domain name to an IPv6 address. The name AAAA is derived from the fact it takes four times as many bytes to store an IPv6 address compared to an IPv4 address. AAAA records are becoming increasingly important as the Internet transitions from using IPv4 protocol to IPv6, to accommodate more unique IP addresses.
What is a DNS CNAME Record?
The CNAME, or the Canonical Name record, is a specific type of DNS record. It is used to map a subdomain or domain name to another hostname.
This is often used when you wish for multiple domain names to lead to the same location. Instead of having to update multiple records if something changes, you update the CNAME record and all associated domains will follow. Essentially, a CNAME record enables a domain or subdomain to point to another domain name, functioning as a kind of redirect.
What is a DNS MX Record?
The MX record, or the Mail Exchanger record, are specifically used for email routing. This record points to the server that receives the email for your domain. When someone sends an email to your domain, their email server will look up your domain’s MX records to determine where to deliver the email. These records often contain priorities, so if multiple records exist, the one with the lowest number is attempted first. This system ensures that your emails get to the right server, and is crucial for your email to function correctly.
What is a DNS TXT Record?
The TXT record, or the Text record, are a type of DNS record that provide text information to sources outside your domain, that can be used for a variety of purposes. The text can be either human- or machine-readable and can include details on the domain, information about the organization, validation codes, etc.
One of the common uses of TXT records is to help prevent email spam. For instance, Sender Policy Framework (SPF) and DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) are two methods that use TXT records to verify the sender of an email and check it wasn’t altered along the way.
What is a DNS NS Record?
The NS record, or the Name Server record, is used to indicate which DNS servers are authoritative for the domain it is listed under. It tells other computers on the internet where to find the DNS information for a specific domain. This record helps in finding the server or servers hosting the domain’s DNS records, leading to the right server when a user wants to access a particular web page within the domain. Every domain must have an NS record in its DNS zone.
What is a DNS SOA Record?
The SOA record, or the Start of Authority record, is a type of record in the Domain Name System (DNS) that contains key information about a domain. It is the record that signals the start of the DNS zone, and it contains information about the zone’s properties. The SOA record includes the primary name server for the domain, the email of the domain administrator, the domain serial number, and several timers relating to the propagation of the domain’s records.
What is a DNS SRV Record?
The SRV record, or the Service record, is a specification of data in the Domain Name System defining the location, i.e., the hostname and port number, of servers for specified services. It is used to establish connections to services without the need to know the exact location beforehand. This includes services like SIP (Session Initiation Protocol), XMPP (Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol), FTP (File Transfer Protocol) and others. The SRV record makes it easier to manage certain services and applications in the DNS by allowing these services to run on any port regardless of the restrictions of firewalls and routers.
What is a DNS PTR Record?
The PTR record, or the Pointer record, is essentially the opposite of an A or AAAA DNS record. While an A or AAAA record is used to convert a domain name or subdomain into an IP address, a PTR record is used to convert an IP address into a domain name. PTR records are often used for reverse DNS lookups, enabling the server to check if the IP address fits with the domain or subdomain name connected with it. This can be particularly useful for spam filters, as spammers often use invalid IP addresses, which will not match up to a domain in a reverse DNS lookup.
The less commonly types of DNS records
Beyond the well-trodden path of frequently used DNS records, there exists a category of less common DNS record types. While they may not be as prevalent in everyday DNS queries, their significance can’t be understated, as they perform specialized tasks that uphold the sophisticated structure of the internet. These less commonly referenced DNS records are like the specialized tools in a toolbox — not needed for every job, but when required, they are indispensable for the task at hand. They may control options for security, specify conditions for traffic routing, or provide important network services information.
What is a DNS AFSDB Record?
The AFSDB DNS record, or the Andrew File System Database record, is a type of DNS record that’s used to locate servers for the Andrew File System (AFS) protocol. AFS is a distributed file system that enables multiple machines to share files over a network. With AFSDB records, client machines can identify and connect to the appropriate AFS servers in order to access files in the network. This type of record is also used to identify Kerberos authentication servers for domain name resolution.
What is a DNS APL Record?
The APL record, or the Address Prefix List record, is a type of data record in the Domain Name System (DNS). It is used to store IP address ranges for a specific domain name and permits a granular definition of IP addressing information within DNS. This includes not only single addresses but also subnets in both IPv4 and IPv6 formats. It is not commonly used as major DNS software do not support it yet and it is considered experimental.
What is a DNS CAA Record?
The CAA record, or the Certification Authority Authorization record, is used to specify which certificate authorities (CAs) are allowed to issue certificates for a domain. It helps to improve online Security. The CAA record contains the domain name, a flag to allow or disallow the specified CA, and an optional section for policy parameters. The overall aim is to prevent the issuance of unauthorized certificates for a domain, thus helping to prevent Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks.
What is a DNS DNSKEY Record?
The DNSKEY DNS record is a data record used in the Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC) protocol. It is used to authenticate and verify the integrity of responses to DNS queries. Essentially, the DNSKEY record contains the public key that a resolver uses to verify digital signatures in the DNSSEC system. Each DNSKEY record is associated with one or more RRSIG, or resource record signatures, which are used to authenticate the records using cryptographic signatures.
What is a DNS CDNSKEY Record?
The CDNSKEY record, or the Child DNSKEY record, is a part of the Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC) protocol which is used to support secure DNS lookup queries. This record is similar to DNSKEY, but is allocated for a child zone in DNS hierarchy. This record enables the child zone to publish its keys to the parent zone directly, assisting in maintaining secure delegation of DNSSEC, and thus playing a vital role in secure DNS communication. The CDNSKEY is crucial for a process known as automated DNSSEC provisioning.
What is a DNS CERT Record?
The CERT record, or the Certificate record, is a type of resource record in the Domain Name System (DNS). This record allows for the association of certificates and related certificate revocation lists to a domain. Internally, it stores the certificate type, the key tag, the public key’s algorithm, and the certificate or CRL in the DNS database. It helps in secure verification of domains and to establish secure communications, commonly used with email encryption and sender verification systems.
What is a DNS DNAME Record?
The DNAME record, or the Delegation Name record, is a type of record in the Domain Name System (DNS) used to redirect a whole subtree of the DNS to another domain. It enables a domain to be reorganized without affecting the rest of the domain names in the subtree, unlike the CNAME record that redirects one specific name to another. The DNAME record basically provides aliases for all the subtrees of a particular domain, not for a single name.
What is a DNS HIP Record?
The HIP DNS record, or the Host Identity Protocol record, is a type of resource record in the Domain Name System (DNS) that allows systems to map domain names to specific hosts based on cryptographic identifiers. This system provides the opportunity for more secure and efficient routing solutions. It addresses limitations around IP-based identity, mobility and multi-homing, without changing the underlying IP protocol. It also provides a way to establish secure communications over insecure networks, improving privacy and making systems more resistant to denial-of-service attacks.
What is a DNS IPSECKEY Record?
The IPSECKEY Domain Name System record, is a type of resource record in the DNS used to hold public key information that can be utilized with the IPsec protocol suite for secure communications over IP networks. This record is used to support a method for securely exchanging IP network layer packets by providing encryption and data origin authentication. It allows a DNS domain name to be associated with a public key, so end hosts can retrieve the key and use it to establish secure communications.
What is a DNS LOC Record?
The LOC DNS record, is a type of resource record in the Domain Name System (DNS) that allows geographical location information to be associated with a domain name. This record was originally designed to facilitate the use of DNS in various location-sensitive applications, such as emergency services or pinpointing the physical location of specific servers. The LOC record provides information like latitude, longitude, elevation, and the size of the area within which the server might be located. However, it’s not widely used and not all DNS servers are configured to return this type of record.
What is a DNS NAPTR Record?
The NAPTR record, or the Naming Authority Pointer record, is a type of record in the Domain Name System that is used for several applications, including SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) and ENUM (telephone number mapping). It enables the DNS to provide information about services available for specific domains, such as email, VoIP, and web services. This record is also commonly utilized in regular expression based rewriting rules of domain names, supporting dynamic resolution of a domain’s protocol, port, and server. However, its implementation can be quite complex compared to other DNS records.
What is a DNS NSEC Record?
The NSEC record, or the Next Secure DNS record, is a type of DNSSEC record used to secure and authenticate the Domain Name System (DNS). This record provides cryptographic assurance that a specific DNS name does not exist. It’s a way to protect against DNS spoofing and other attacks by proving the nonexistence of a name or a type. It also lists all the record types that the owner name has. The NSEC record links to the next owner name in the zone which helps to prevent zone enumeration.
What is a DNS RRSIG Record?
The RRSIG DNS record is a type of record in the Domain Name System (DNS) used for DNS Security Extensions (DNSSEC). This record stores the digital signature of another DNS record set. By verifying this signature, a DNS resolver can check the authenticity and integrity of the data in the corresponding DNS record set, ensuring that it hasn’t been tampered with. This mechanism is part of the DNSSEC protocol, which adds a layer of security to the DNS by offering authenticity and data integrity, but not confidentiality.
What is a DNS RP Record?
The RP record, or the Responsible Person Record, is a type of record that holds data that specifies an email point of contact for the domain. It also contains the hostname to a TXT DNS record (which commonly contains additional human-readable information about where to send information regarding the domain.) Using the RP record can be advantageous from a management perspective, as it provides another level of control and information regarding domain contacts.
What is a DNS SSHFP Record?
The SSHFP record, or the Secure Shell Key FingerPrint record, is a type of record that holds SSH fingerprint data. It’s designed to help prevent man-in-the-middle attacks. It holds a cryptographic hash generated from a server’s public key, allowing SSH clients to verify the server’s identity before making a connection. This record only works for DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions) enabled domains as it relies on the additional security provided by DNSSEC for authenticating records.
Mastering the Art of DNS Records Inquiry
Embarking on a DNS records lookup can provide crucial insight for those who are managing websites, diagnosing network issues, or simply seeking to understand more about how the Domain Name System operates. A DNS record lookup is particularly useful when you’re configuring domain settings, validating data for a migration, or investigating service disruptions. The process is pretty straightforward: you simply just need to input the domain in question into a lookup tool, and it initiating the retrieval of its DNS records.
For anyone in need of checking DNS records without digging through complex backend systems, numerous online tools have been crafted for this purpose. These instruments of domain exploration are developed with simplicity in mind, ensuring that even those with minimal technical knowledge can perform a comprehensive DNS records lookup. One such tool that is available for use is our own DNS & WHOIS Lookup. Our offers an intuitive interface to help both novices and seasoned professionals in initiating a DNS records lookup efficiently – and with just a few clicks, the requested DNS information is made readily accessible.
In short, the ability to check DNS records through a DNS record lookup tool is a user-friendly way to gain a deeper comprehension of domain configurations, improve your website’s reliability, and bolster security measures. And while regular checks are not a necessity for everyone, having the knowledge and the ability to conduct a dns record lookup when needed is a skill that can save time and prevent potential issues down the line.